Digital transformation may seem like a simple and straightforward process of incorporating new technologies into our business, but it is a more complex and profound process. Transformation involves understanding the characteristics of today’s society in order to be able to incorporate the necessary changes into our business to adapt it to the new context. It is not just about using ICTs is understanding how they have changed market conditions and how they affect our business. But don’t worry, in these lines, we tell you everything you need to know step by step in a simple way.
What is digital transformation?
Digital transformation is about embedding a fully digital approach to all areas of the business and focusing our business fundamentally on the customer and the customer experience. Digital transformation involves using AI, automation technologies, hybrid cloud and other digital technologies to collect and analyse data, to drive intelligent workflows and better decision making and, above all, focus on the customer experience.
The whole flow of information and the use of these tools can also help to uncover new business opportunities or threats in the future.
Here are some very interesting podcasts that address digital transformation from different perspectives
Digital Transformation Podcast
We will now take a look at the state of digital transformation in a country like Spain:
What is the state of digital transformation in this country?
According to the DESI (Digital Economy and Society Index) which measures 4 different indicators: human capital, broadband connectivity, the integration of digital technologies by companies and digital public services, Spain is in 9th position among the member countries at the end of 2021.
If you want to know more detailed data about the state of digital transformation in Spain, please click here.
Understanding the 21st-century customer and their context is fundamental to understanding digital transformation. The digital era has very different rules from the pre-2008 world. The customer has become a more demanding actor, equipped with knowledge and technologies that allow him/her to have access to much more information about any type of purchase and decision making. Moreover, the possibility of sharing information and experiences makes them critical customers and an actor to care for more than ever.
Transformation is a complex process, which goes beyond the use of IT services, what we know as digitisation, to clarify concepts and better understand digital transformation, here are the differences.
What is digitisation?
Digitisation is the process by which we transform analogue processes and convert them into a digital process, such as using computer documents, digital signatures, scanning documents or cloud storage services.
Digitalisation is a process that has gradually become more and more integrated in companies thanks to the innovation and democratisation of technology.
Differences between digital transformation and digitalisation
A very important feature of digitisation is that it does not change the procedures, but adapts these processes from the analogue version to the digital version.
Digitisation converts and encodes data and information into a digital format while digital transformation is an internal process of companies that goes beyond business processes.
Digital transformation seeks to generate more value for its stakeholders, i.e. all the actors involved in a company or organisation: customers, suppliers, employees, shareholders etc.
The ultimate goal of digital transformation is to adapt to the current context, in an interconnected and hyperactive world. Digitalisation plays a fundamental role, and without it, it is difficult to understand digital transformation, but only one more pillar of business success.
To delve deeper into digital transformation we will look at how digitisation is being tackled in different sectors and the significant value they bring to each of them.
Digital transformation in business
Digitising a company means using digital tools and technologies to make business processes more efficient and the company itself more competitive.
To achieve this, digitisation varies substantially depending on the nature of the company, although some common processes can be found in most companies:
- Digitising company documents (orders, invoices, inventories, warehouse records, business correspondence, etc.) means dematerialising: moving from an analogue medium, such as paper, to a digital one. By doing this, the very essence of the documents is changed and a wide range of possibilities for improvement are opened up for the company.
- Training and awareness of workers. Workers must know and be trained in the use of these technologies, see change as an opportunity for improvement and be aware of the possibilities of the digital world as opposed to the analogical one.
- Social media. The importance of giving planned and professional content to social networks and understanding it as a means to engage in conversation with customers.
- Sustainability. It is impossible to understand digitisation and digital transformation without society’s concern for the environment, climate change and carbon footprint.
- Optimises human talent management to use and distribute resources more efficiently.
Digitalisation in the industry has brought about a major revolution through connectivity and data, significantly improving productivity, quality and cost of processes.

Connectivity and interoperability
Connectivity and interoperability of manufacturing, logistics, custom design and customer areas enable the manufacture of customised products and services at affordable prices.
The connection between an object and person
At any time and in any place, tAt any time and in any place, everything is connected thanks to the Internet of Things. Innovation in both hardware and software has enabled total interaction between all actors, allowing the automation and optimisation of many processes.
Sustainability
More and more people and companies are concerned about the environment and the impact of their activities on it, such as their carbon footprint.
Internet of behaviours
The connectivity between objects, machines and people, i.e. the Internet of Things, has enabled the development of the internet of behaviour, thanks to the analysis of industry data and the use of artificial intelligence to improve productivity and increase and improve efficiency as never before. Here you can learn more about the Internet of behaviours.

Optimisation of administrative processes
Digitalisation can significantly improve the productivity of administrative processes. A clear example is a TMS (Transport Management System), a transport management software. In other words, a type of logistics system that allows a large part of the logistics process to be automated, thereby increasing the efficiency of processes and improving service.
Real-time tracking processes
Allow customers to know the exact location of their order and the waiting time until delivery. Real-time tracking processes provide suppliers with the traceability necessary to know exactly the remaining times for each of the following processes.
It also allows delivery routes to be planned with knowledge of the next shipments, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Some of the technologies that are being incorporated in this type of process are RFID, E2E (tracking and traceability through transport companies’ online platforms) and blockchain (technologies that manage information quickly and securely).
More efficient and dynamic supply chains
Digital planning processes allow supply chains to be dynamically modified and transformed, adapting them to markets and their changing demand. Thanks to software with advanced algorithms and Data Lake technology, they enable the intelligent prediction of sales by cross-checking information with all departments of the organisation. This helps to plan production, transport and storage and to design the transformation of the supply chain.

Security
Due to a large amount of data and its flow through the network, information is susceptible to risks such as information leaks, due to the insecurity of networks, loss of availability in the service or the manipulation of these causing problems in planning.
For this reason, industrial digitisation projects for the value chain and the integration of its applications should incorporate cybersecurity in the design. To help in this task, there are platforms such as the Centre for Industrial Cybersecurity (CCI) which, as an example, has created RECIN, the Cybersecurity Requirements for Industrial Projects platform.
This platform allows modelling automation projects in the supply chain and recommending cybersecurity patterns from an affordable catalogue of requirements that include regulations and standards.
There are also other projects such as Nymiz, the Spanish startup that develops one of the best data anonymisation and pseudonymisation software.

Digital transformation in Human Resources
Human Resources management in companies has traditionally been an area of constant improvement and work. Selecting the right staff, managing resources, and coordinating workers are indispensable tasks for the functioning of an organisation.
Digitalisation in the field of HR is essential to optimise the management of human talent in order to use and distribute resources more efficiently. It also turns human resources departments into direct agents of change in organisations, taking a more active and leading role in decision-making.
Digitalisation generates new personnel management strategies and action plans for decision-making. In essence, the time optimisation afforded by digitisation drives towards greater forward planning.
One of the technologies that have had the greatest impact in the area of HR is AI, due to its ability to improve processes.
Artificial Intelligence in HR. What is HR Analytics?
Data Analytics is a process of data analysis of both employees and the company’s environment through Big Data Analytics. Thanks to this methodology it is possible to obtain valuable information that is very necessary for decision making. Some of the uses can be:

Recruitment processes
Thanks to AI, it is possible to use different algorithms to, for example, perform initial filtering and offer the most suitable profiles for the position offered. The reduction of time and effort is a clear optimisation of resources and time, both for companies and candidates.
Tailored offers and targeted selection processes make it easier to attract talent and select the best people for the job.
Predictions
The data with the information available from a workforce can be processed in its entirety by Artificial Intelligence. It is a source of relevant information about the performance, status and productivity of an organisation.
AI allows predictions to be made on issues such as demotivation, absenteeism, stress-related sick leave or depression.
In addition to this, AI can be an excellent tool in building an Employer Branding strategy. By interpreting data more quickly and efficiently, AI itself can be programmed to improve the employee experience. It is possible, for example, to use AI to provide employees with more accurate information and thus aid talent retention.
Training
More and more applications are relying on AI to help employees improve their skills and competencies.
LMS or micro-learning-based software can be incorporated so that each employee can learn small training capsules on a daily basis in no more than 15 minutes a day. One way to use this system is through “interactive games” to learn in an engaging and enjoyable way.
In short, human resources can be a major player in the involvement of digitalisation. The human factor can generate a whole change in the corporate culture of organisations and is therefore essential for digital transformation.
Banking digitisation
Digital transformation is an unstoppable dynamic in many economic sectors, but in banking, it offers opportunities in both the front and back offices. In the front office, the most obvious use is to meet customer needs more efficiently.
In the back office, it can be used as a way to achieve efficiency improvements to optimise the service and quality offered to users.
The development and application of models based on data management and AI are becoming key elements to improve financial services. These models make products more efficient and tailored to customers’ needs and should reinforce aspects such as security and trust.
Technological progress, but regulated and safe
The pace of technological advancement makes it necessary for both banks and authorities to work together to understand and fit the use and application of AI into regulated activities, so that its full benefits can be realised, without compromising the safety and security of customers.
The financial world is always one of the fastest evolving, so it must also strive to maintain the basic principles of consumer protection, financial stability and market integrity. In addition, balance and competitiveness between new entrants based on these new technologies and traditional banking must be ensured.
If you want to know more about the use of AI in the banking sector we leave you this link from UK Finance
Technologies used for digital transformation
Some of these technologies have already been discussed in previous examples, but here is a summary of some of the most innovative technologies of the moment.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the provision of on-demand computing resources, from applications to data centres, over the Internet on a pay-as-you-go model.
IoT and IoB (5G and 6G)
The Internet of Behaviour is a logical consequence of the Internet of Things. It consists of the analysis of data obtained by all devices connected to the internet in order to recognise behaviours and patterns of interest.
Big data
Big data consists of large and complex datasets, usually from computer data sources. These were unmanageable until a few years ago, but nowadays, they can be very useful thanks to software analysis and artificial intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the ability of a machine or software to exhibit human-like capabilities, such as reasoning, learning, creativity or the ability to plan. Through AI, technological systems can perceive their environment, interact with it, and can solve problems and act accordingly.

Machine learning
Machine learning is the area of Artificial Intelligence, in which computers apply statistical learning techniques in order to automatically identify patterns in data. Therefore we can say that it is machine learning as automated learning or machine learning.
Business intelligence
We can define business intelligence as the set of tools and processes that enable the preparation, mining, management and visualisation of data. The objective is to know and make the best possible decisions in the company.
Digital marketing and e-commerce
We could define it as any type of marketing that uses any digital tool at its disposal to facilitate and obtain better results. In this way you can also buy and sell more products through the internet, what we call e-commerce.
Blockchain applied to digital transformation
The blockchain is a technology that uses cryptographic techniques to streamline complex transactions. Through the verification by all users of all blocks, it is possible, for example, to eliminate intermediaries in a monetary transaction. This is a technology with many possibilities for the future, you can find more information on this link.
3D printing or additive manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a set of processes that generates objects by adding material to layers that correspond to successive cross-sections of a 3D model. Plastic and metal alloys are the materials most commonly used for 3D printing, but the process can work with virtually anything from concrete to living tissue.
These are some of the technologies that are already being used by many companies to manufacture the future.
The key is to identify which of them or the combination of them can be useful for our business.
We live in a world in continuous evolution, so it is possible that in the coming years’ new technologies will emerge around the previous ones and other totally innovative ones that will revolutionise the market. Therefore, another characteristic of digital transformation is an active and continuous learning mentality, a real interest in keeping up to date and in innovation.
Benefits of digital transformation
If my business works, why would I spend money on a digital transformation?
Digital transformation is never an expense but an investment that will bring your business a large number of feasible benefits:
Improving productivity
Automating processes allows tasks to be carried out more efficiently and autonomously. It also allows the status of projects to be known at all times and helps to manage time.
Employees carry out their tasks in a much more agile, autonomous and efficient way, control the status of their projects in real-time and manage time appropriately.
Identifying new business opportunities
The Internet has become a great ally to expand our business. Having an attractive website and active profiles on social networks contributes to improving our presence. Interaction with customers and other companies can lead to the identification of new business opportunities.
Reducing time and costs
Improving productivity is a great time and cost saver in all departments of the organisation. Reducing production lead times, decreasing the margin of error and increasing business competitiveness, in turn, increases business opportunities.
Reducing risks
The automation of different stages of production allows us to be aware of the situation we are in at all times, drastically reducing the possibilities of failure and increasing the capacity to respond to errors.
In this sense, digitisation helps to analyse and detect possible future problems in order to assess them and establish an action plan to prevent such failures from eventually occurring.
Improving communication
Digital transformation helps to foster communication both internally and externally, horizontally and vertically, which in turn improves all aspects of the organisation.
Improving the customer experience
As we said before, we live in a world where the customer is increasingly critical, is better educated and has a lot of information at their fingertips with a simple click.
Using new technologies allows us to offer a more personalised and unique experience according to their tastes. In addition, knowing the market better than ever before allows us to offer products and services that better meet customer needs.
There are different ways to measure customer satisfaction and here are some examples of them.

Finding new markets
Digitising the company helps to internationalise the products or services offered. This can not only help to generate more profits but also reduce risks and increase competitiveness.
Collaborative work and innovation
Interconnection between departments and with other companies favours fluid communication and helps to work together between all areas of the company and even with other organisations or suppliers, creating a more satisfactory communication.
All this fluid communication in turn helps the emergence and capture of new ideas, facilitating innovation. In addition, technology helps us to be more up to date with what is being done in the market and, thanks to constant evolution, helps us to keep learning day by day.
Decentralisation and family reconciliation
Digitalisation makes it possible to work from anywhere, allowing mobility and decentralisation of work. It also helps employees to reconcile work and family life, making it easier for them to stay with the company.
Analytical skills
Implementing digital tools allows us to monitor many operations and have much more information available to us. Having all this information will allow us to deepen the data analysis capacity of all areas of the company, helping in decision making and productivity.
By committing to digital transformation, it is possible to deepen the analysis of data from all departments of the company. Thanks to the implementation of new data collection systems, work is better managed and, consequently, the right decisions are made at all times.
Responsiveness
Quick reaction to potential issues and problems is a key differentiator compared to the competition. Thanks to data collection and analysis, it is easier to respond and anticipate decisions and in turn to make the most appropriate decisions.
To better understand the importance of digital transformation, let’s look at successful examples of companies that have undertaken it.
Examples of successful companies in their digital transformation
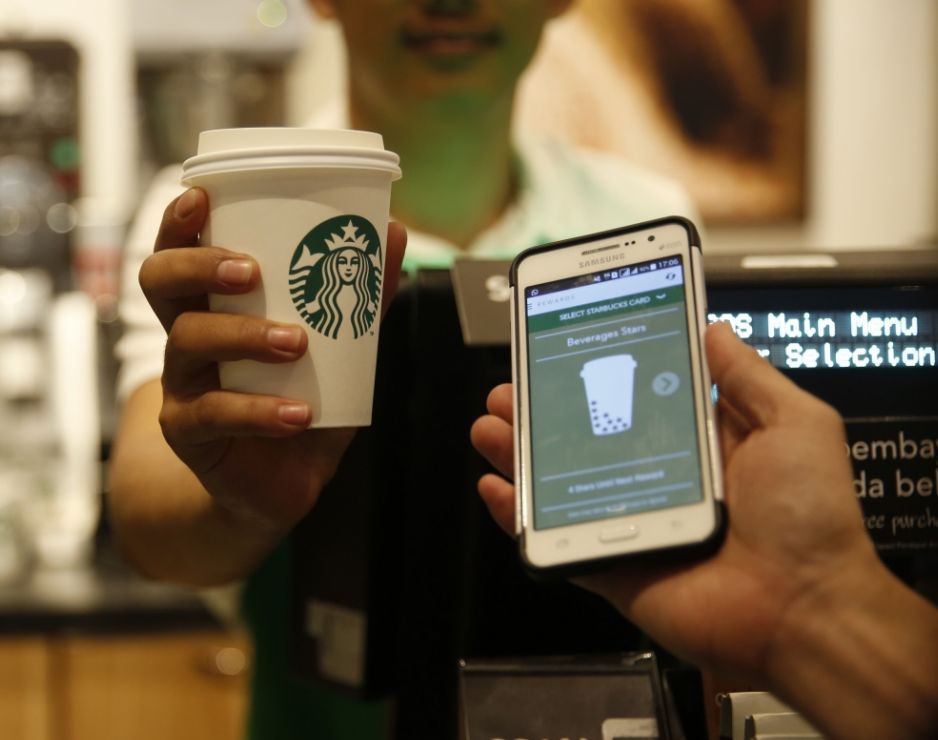
Starbucks
This well-known coffee shop company focused its efforts on a mobile application. In this mobile app, they have created what they call an end-to-end platform to focus their efforts on customer experience and customer loyalty.
The application also allows you to collect data and consumption patterns. Thanks to this application they can, for example, warn customers that their employee is going to take a break and it is the customer who goes to get their coffee or offer rewards to their customers for their commitment and consumption in their cafeterias. This is a clear example of how to use big data to the benefit of the company.

Ford
The automotive industry has faced a major challenge with the need to reduce combustion engines and incorporate hybrid or electric engines into vehicles. Ford was on the verge of bankruptcy in 2006 but is now in a privileged position in the market. It unified the entire company and focused on three areas: quality, data and innovation.
Investment in these three areas has led to technologies such as Ford SYNC, which helps you control your vehicle through voice commands, and Ford Touch, which allows you to do so without taking your hands off the wheel.
Its commitment to digital made it the only car brand present at the first Mobile World Congress.
Inditex
The success of this company cannot be understood without understanding its digitalisation. Inditex opted for big data to optimise its inventory and has one of the most accessible and practical websites.
The methods that Zara developed for its big data have been the use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, which is a system for storing and retrieving data through tags, or as Zara does, through barcodes or smart cards that accompany the products.
This technology has allowed the group’s companies to monitor the time from when a garment is in stock until it is sold. It also allows them to collect data such as what type of garment sells best, as well as the fabric it is worn in, and its colours.
All this data helps the company in the creation of new collections and customer satisfaction as well as in the logistics of the company itself. In this article, you can read more in-depth about Zara’s success and its use of big data.
Zara has recently unveiled its biggest store in the world, which is loaded with new technologies such as smart screens and virtual fitting rooms.
Successful companies are a good example of the importance of digital transformation. We can understand the importance of digital transformation even better if we look, on the other hand, at those companies that failed to adapt to the new times.
Examples of companies that did not understand digital transformation
Atari
Since its launch in 1977, the Atari 2600 console sold more than 42 million units worldwide. However, by 1982, the company went through a crisis from which it could never recover.
The fundamental difference between Atari and its competitor, Nintendo, which it eventually surpassed by far, was the focus of their efforts. Atari decided to focus on the development of consoles while Nintendo focused on the development of better video games. As a result, with the release of Mario Bros, Nintendo eventually surpassed Atari by a wide margin.
Kodak
In 1881, the company was founded with a novel concept that made it successful in the market: to simplify the process of printing photographic plates. In the 1960s, 90% of both film and cameras were Kodaks, but in 2012 the company went bankrupt.
Kodak did go digital, creating the first digital camera in 1975. But because it had a monopoly on film, it decided that it was not a good decision to market this product.
The competition did not hesitate to market and bet on digital photography, and in less than two years Kodak lost its hegemony.
Blockbuster
Blockbuster was a movie and video rental company that rented movies and videos in modern and attractive locations. In 1994, with a growing billion-dollar business, the company was acquired by Viacom for $8.4 billion.
The company failed to see the change in the market trend coming, in 2000 a small movie delivery company, Netflix, proposed to join forces to create a streaming platform. Blockbuster turned down the offer, and in 2010 filed for bankruptcy.
Nokia
The Finnish company was the leader in phone sales for more than 14 years, however by 2011 it had lost 40% of its global market. This was due to Apple’s introduction of the first iPhone in 2007 and the launch of the Android operating system in 2008. Nokia kept its products focused on businessmen and executives, failing to see that mobiles would become a fundamental tool for all sectors of the population. Something similar happened to the Blackberry company.

Olivetti
Unlike other companies, this typewriter brand knew how to be at the forefront of technological development, manufactured electric calculators, developed the first desktop computer and launched the first netbook in history.
However, it made the mistake of wanting to maintain its monopoly and developed closed software, which meant that its computers were not compatible with others, generating a high cost for its users. Eventually, the brand decided to get out of the computer business.
There are many cases, especially in recent decades, of companies that either did not know how to innovate or made the wrong decisions and here are some more examples.
Digital transformation is a complex process in which mistakes can be made. The good news? The good news is that nowadays there are many aids and companies specialising in this field.
Support for digital transformation
Digital transformation can be a difficult process to tackle if you do not have the necessary knowledge and advice to carry it out correctly. That is why we are going to see some help from institutions
Digital Kit. This is an initiative of the Spanish Government, which aims to subsidise the implementation of digital solutions available on the market in order to achieve a significant advance in the level of digital maturity. This programme is part of a much more ambitious EU plan to boost the digital transformation of companies across Europe: the Next Generation funds.
Centre for Digital Transformation. The Centre for Digital Transformation helps businesses understand the far-reaching organisational implications of the digital revolution.
Government backs UK entrepreneurs with tech support and software to help them grow. The program “Help to Grow” Digital scheme launches to support small businesses with discounted software and free advice.
Addressing the digital transformation can be a very broad topic depending on the characteristics of each company, so it is also advisable to have the support of specialized and experienced consultants. From Opensistemas we encourage you to contact us if you are interested in taking your company into the future.
Strategies for digital transformation
As for any important activities within a company, we must follow a well-defined roadmap to avoid making mistakes. The strategy may be very different depending on our company and the current degree of digitisation, but in broad terms, we can make a few basic points
- Situation analysis With this information we can know the degree of digitalisation of our organisation. Prepare a report on the current state of your company, including company history, SWOT analysis and employee characteristics (such as age, training, etc.).
- Hire help. The scale of the transformation may be beyond our expertise, so it is essential to hire people or digital transformation companies, such as OpenSistemas.
- Define objectives. Establish defined, measurable and achievable objectives.
- Drawing up a plan. Based on the established objectives, we must establish a plan of concrete actions to achieve each of the objectives In this phase we must choose the most useful tools for carrying out each of the objectives.
- Action plan. It is important that you can assign the corresponding tasks to the people involved in the project.
- Monitor and measure. Measure your actions during and after the implementation of the plan. This will allow you to identify your strengths, weaknesses and future actions. You will know if you have been successful or if something did not work well.
Courses on digital transformation
In addition to the help of professionals, it is always interesting to be trained in areas that are currently trending, both to know how to differentiate good technology providers and to develop your own internal projects. Here are some of the digital transformation courses we have selected:
Digital Transformation and Innovation courses. London Business School
Executive Education Digital Transformation program. UC Berkeley
Digital transformation. Coursera
Digital tranformation. Cornell










