Cloud Computing: What is and what is it for?
The last few years have been a revolution in terms of the emergence of new technologies. Concepts such as Big Data, Cloud Computing, are becoming more and more widespread, both in personal and professional use. However, for many people, these terms are still the great unknown. In this article, we tell you what is and what is the use of Cloud Computing.
The truth is that we use this type of technology in our daily lives in a much more assiduous way than we think. It is possible that if someone asks you for the definition of “Cloud Computing” you do not know very well what to answer, however it is essential to assimilate and understand this concept if you do not want to be left behind in the digital transformation that we are living.
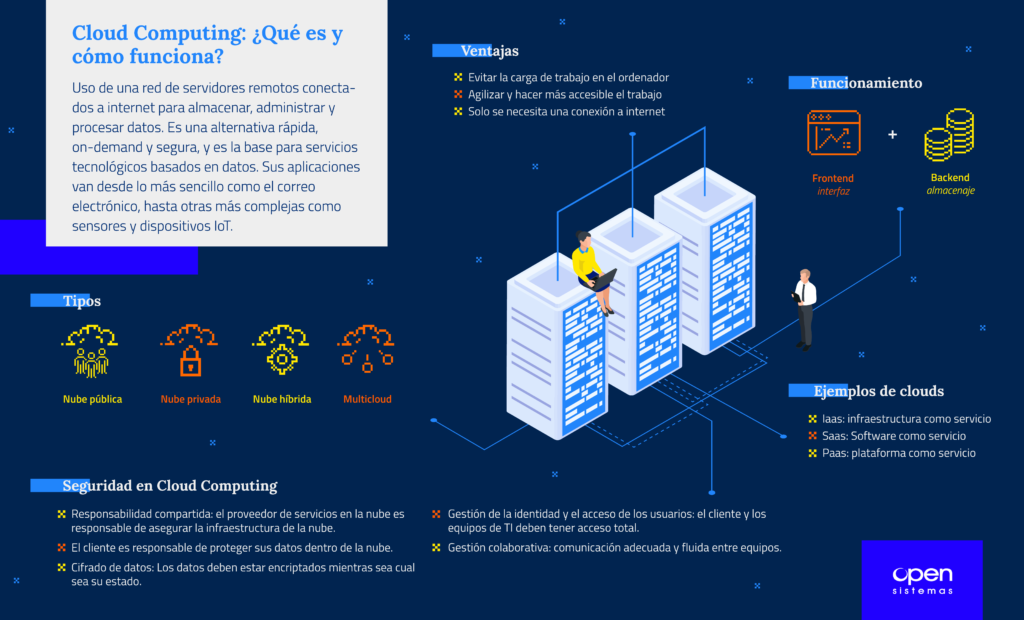
Cloud computing definition: consists of offering computing services over the network using cloud storage. With this type of service, the user does not have to install anything on his computer, however, he will have access to different services (from the most everyday to the technical).
What is Cloud Computing? And what are the advantages of cloud computing?
To explain this concept as simply as possible, we will use an example: in this case e-mail. More or less all users use e-mail and the truth is that it is a cloud computing service. That is, you use e-mail without having to install anything on your computer, and also for free
The same applies to applications that do not need to download anything. This is because of their cloud storage or their business management systems. This technology is becoming increasingly important in our lives.
Cloud computing is a fast, ondemand and secure alternative for many services.
Let’s see more characteristics of cloud computing that we summarize in the illustration above “cloud storage illustration”.
What is cloud computing for?
One of the greatest uses of this technology is to avoid the computer having to assume a heavy workload when running applications. Cloud storage speeds up the work, making it accessible and without overloading the computer of the user who is using the service.
The only thing the user will need is access to the Internet (as if it were a website). The cloud will take care of the rest of the work, simplifying everything.
Without a doubt, the advantages of cloud storage today are indisputable. Not only are the resources available to the user multiplied, but it also avoids the cost of unit licences, making them accessible to different people on the team.
How Cloud Computing works?
In Cloud Computing systems, we can find two different parts within the system:
- The Frontend (or user interface).
- The backend (i.e. the cloud service itself).
When we talk about the user interface, we will include the computer network, and also the application to access the cloud service. Thanks to an interface the user will be able to connect to the backend through the internet.
When we talk about backend we mean all the systems that the cloud uses for information storage (including servers and computers).
All the different gears, are in charge of connecting to a central server that will manage the operation of the system. This will use key protocols and middleware software to facilitate the connection between the computers that communicate with each other.
This complex (but apparently simple) system brings great benefits to both users and companies.
Cloud computing examples
In summary, we could classify three types of Cloud Computing, which are the most common examples:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Google Cloud Computing or Amazon Cloud are examples of companies that offer a suite of cloud computing services, specifically designed for end users.
But if you have in mind how large enterprises work in the cloud, then those cloud computing services are probably being provided by technology providers that specialise in cloud and digital transformation.
If you want to learn more about how to access cloud services, read our use case on how to migrate to the Google Cloud.

Types of Cloud Computing
Public cloud
Public clouds are cloud environments that are typically built on an IT infrastructure external to the end user. Major public cloud providers include Alibaba Cloud, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, IBM Cloud and Microsoft Azure.
All clouds become public when environments are partitioned and redistributed among multiple users. Pricing structures are no longer defining characteristics of public clouds.
The OS-less IT infrastructures used by public cloud providers can also be extracted and sold as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), or they can be transformed into cloud platforms and sold as Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Private clouds
These are cloud environments that are exclusively dedicated to an end user or group, typically running behind their firewall. Clouds become private when the underlying IT infrastructure is dedicated to a single customer with completely isolated access.
Today, companies design private clouds in third-party leased data centres that are located off-site.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private cloud environments. It connects an organisation’s private cloud services and public clouds. In a single, flexible infrastructure it allows the organisation’s applications and workloads to run.
The goal is to provide an organisation with the flexibility to choose the optimal cloud for each application or workload and to move workloads freely between the two clouds as circumstances change.
This enables the organisation to meet its technical and business objectives more effectively.
Using a hybrid cloud is often more cost-effective than using only a separate public or private cloud.
Multicloud
Multicloud is the use of two or more clouds from two or more different cloud providers.
The advantages of using a multicloud include avoiding dependency on a single provider and access to more applications and innovation.
The main disadvantage of having different clouds can be the difficulty of managing each with its own tools.
Multi-cloud management platforms offer visibility of multiple vendor clouds through a central dashboard. Here, development teams can see their projects, operations teams can monitor clusters and nodes, and cybersecurity staff can monitor threats.
Cloud Computing Security

Contrary to what it might seem, the security offered by cloud service providers is outperforming on-premises security solutions.
While cyber security services in the cloud are secure, they require different procedures and employee skills than traditional IT environments. Some of the recommended security practices are:
Shared responsibility
Typically, the cloud service provider is responsible for securing the cloud infrastructure. While the customer is responsible for protecting its data within the cloud. In addition, it is important to clearly define data ownership between private and public third parties.
Data encryption
Data must be encrypted regardless of its status. Customers must maintain full control over security keys and the hardware security module.
Identity and user access management
The customer and IT teams must know and have full visibility of access to the network, devices, applications and data, in order to know the status and processes being carried out.
Collaborative management
Adequate and smooth communication and clear and understandable processes between IT, operations and security teams are important. This will ensure secure and sustainable cloud integrations.
Security oversight
You need to understand all the regulations applicable to your industry and set up active monitoring of all connected systems and cloud-based services.
This will allow you to maintain visibility of data exchanges between public, private and hybrid cloud environments.
More useful examples of using Cloud Computing

CRM and ERPs
One of the most common cloud computing solutions for companies is software dedicated to customer relationship management.
Sales and marketing, the so-called CRM (customer relationship management) or ERPs (Enterprise resource planning or enterprise resource planning system).
Databases
The creation of databases for storage and their rapid management.
Companies are increasingly dependent on data and its analysis, which is why the creation of these databases and their management systems is essential.
Virtual desktops
They allow access to an operating system and a remote desktop through the cloud.
By connecting to a computer from a remote computer, for example, we can work as if we were in the office.
Thanks to this cloud computing service, you can work from practically any location with an Internet connection, with all the advantages that this implies.
Moreover, as the virtual desktop is hosted on a server, it is possible to work with a less powerful and up-to-date computer.
Other uses of Cloud Computing
There are also many other uses of cloud computing that vary and can be adapted to each of the sectors and characteristics of companies. :
- Office suite
- Back-up copies
- Hosting services
- Data processing centre
- Data storage and transfer

The role of Cloud Computing in the Digital Transformation of Companies
Cloud computing is a key component in the digital transformation of enterprises, as it is the first source of on-demand delivery of computing resources – from applications to data centres, over the Internet and on a pay-as-you-go model.
This allows companies some new possibilities to enhance their existing business, generate competitive advantages or open up new revenue streams. For example:
- Digitise resources and optimise processes.
- Incorporate other technologies to optimise the business, such as a data lake or digital twin.
- Solving complex problems with the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
- Have extended teams or outsource resources, improving their technology-related costs.
In general, implementing digital tools or cloud solutions allows us to monitor many operations and have much more information available to us. Having all this information will allow us to deepen the data analysis capacity of all areas of the company, optimise its processes and help in strategic decision making.









